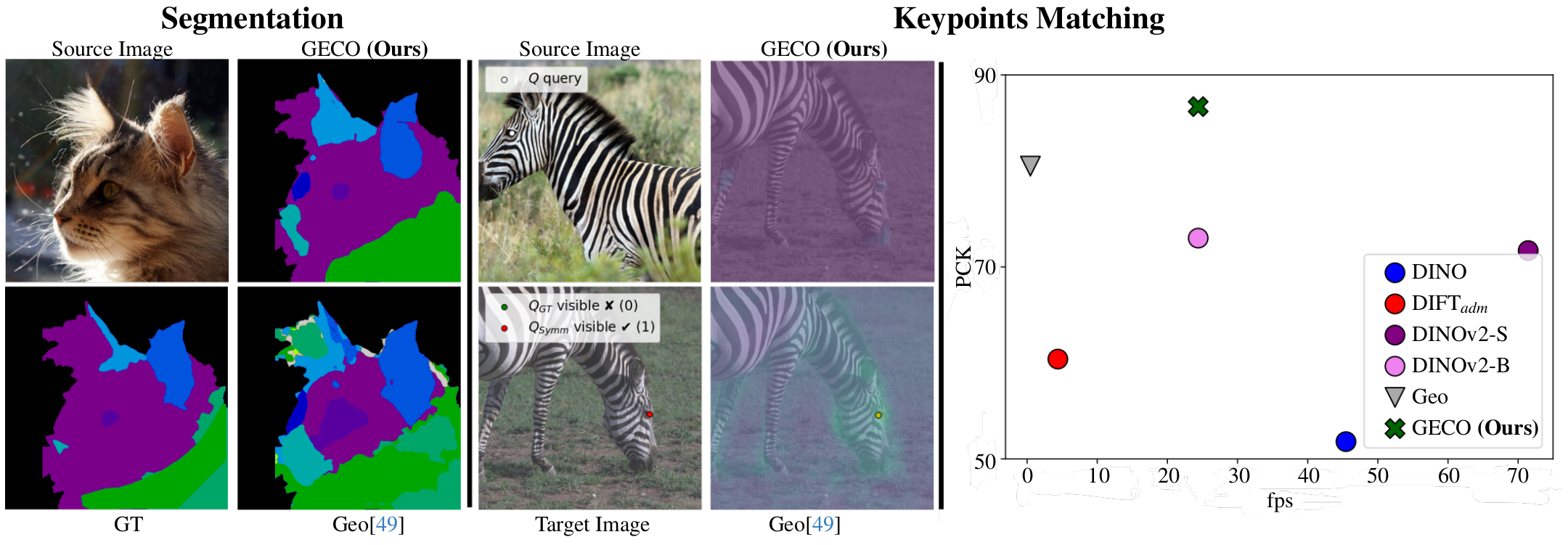
GECO: Geometrically Consistent Embedding with Lightspeed Inference
Recent advancements in feature computation have revealed that self-supervised feature extractors can recognize semantic correspondences. However, these features often lack an understanding of objects' underlying 3D geometry. In this paper, we focus on learning features capable of semantically characterizing parts distinguished by their geometric properties, e.g., left/right eyes or front/back legs. We propose GECO, a novel, optimal-transport-based learning method that obtains features geometrically coherent, well-characterizing symmetric points. GECO uses a lightweight model architecture that results in a fast inference, capable of processing images at 30fps. Our method is interpretable and generalizes across datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance on PFPascal, APK, and CUB datasets improving by 6.0%, 6.2%, and 4.1% respectively. We achieve a speed-up of 98.2% compared to previous methods by using a smaller backbone and a more efficient training scheme. Finally, we find PCK insufficient to analyze the geometrical properties of the features. Hence, we expand our analysis, proposing novel metrics and insights that will be instrumental in developing more geometrically-aware methods.
Project Page | Paper | Code | Video | Citation
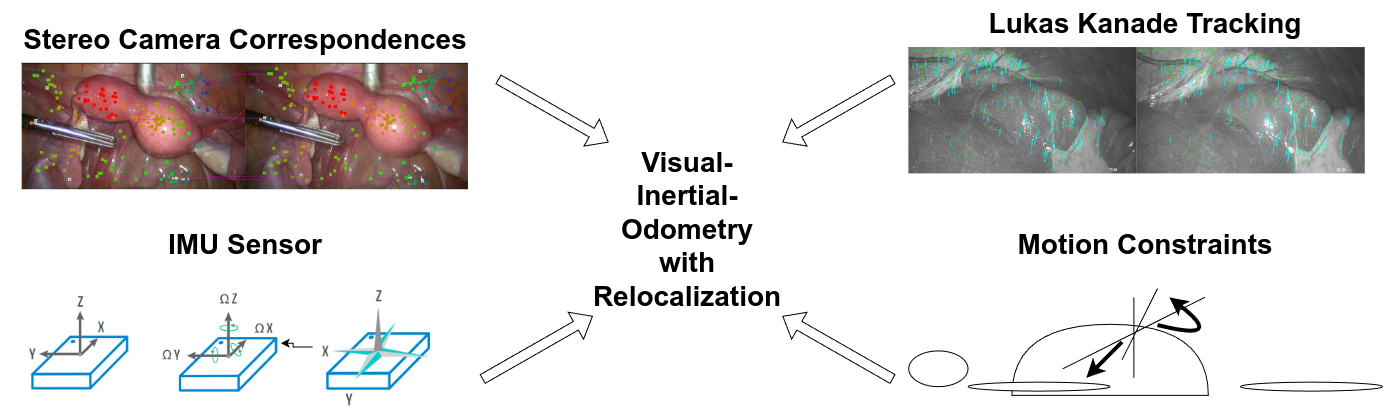
Constrained Visual-Inertial Localization With Application And Benchmark in Laparoscopic Surgery
We propose a novel method to tackle the visual-inertial localization problem for constrained camera movements. We use residuals from the different modalities to jointly optimize a global cost function. The residuals emerge from IMU measurements, stereoscopic feature points, and constraints on possible solutions in SE(3). In settings where dynamic disturbances are frequent, the residuals reduce the complexity of the problem and make localization feasible. We verify the advantages of our method in a suitable medical use case and produce a dataset capturing a minimally invasive surgery in the abdomen. Our novel clinical dataset MITI is comparable to state-of-the-art evaluation datasets, contains calibration and synchronization.
Project Page | Paper | Video | Citation